
In the context of the Project Management Professional (PMP) exam, the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) holds significant importance in helping project managers assess whether requirements and their respective deliverables are aligned with the business purpose. After project initiation, stakeholders are engaged to collect or elicit requirements. In addition to requirements collected from stakeholders, requirements can also originate from other sources, such as compliance documents. All these requirements serve a specific business purpose. Throughout project execution, these requirements are implemented through deliverables, and it is crucial for both the requirements and deliverables to align with the overarching business goals. So, requirements and their respective deliverables should map back to the business goals. So how does the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) helps here?
Understanding What is Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM)?
The Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) acts as a grid, connecting requirements from their origin (Business Need) to the deliverables that satisfy them, thereby preserving the integrity of the requirements. So, how is requirement traceability achieved? This is achieved through backward tracing of requirements to their origin and forward tracing to their respective deliverables. The RTM demonstrates how a deliverable fulfils a particular requirement while serving its corresponding business goal. Recognizing that a deliverable can fulfil one or more requirements is important. For instance, a deliverable might satisfy 20 out of 100 requirements. In such cases, the remaining 80 requirements may be addressed by a different set of deliverables. The Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) provides a comprehensive overview of how all 100 requirements are met by their respective deliverables. It illustrates the connections and relationships between each requirement and the specific deliverable that fulfills it.
Illustrating Traceability of Requirements using Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM):
The Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) is created based on specific project need. It may not present every single elicited requirement; instead, it may focus on tracing and monitoring the requirements that are chosen for tracing for achieving the specific business objectives of the project.
The grid you are looking at here is just an example; the release id is a unique identifier for each release. This release includes high-level requirements which are to be released. Test cases have been designed for these requirements. Also, design components are there which support these requirements. Finally, these requirements are completed, and a product capsule is created.

Here you can see that you can trace this product deliverable back to the source, which is its business need and also, this business need can be traced to its final deliverable. Both forward and backward traceability.
RTM can be used both in Agile and predictive Life Cycle approaches. Both types of projects were initiated due to some business needs. In Agile projects, the emphasis is on incremental delivery and continuous stakeholder validation. Due to the visibility and continuous validation of deliverables, the reliance on a Requirement Traceability Matrix is often minimized. However, in Agile projects, you can still observe natural traceability flow from the product backlog item to its corresponding sprint backlog and ultimately to the delivered increment. This organic traceability serves as a means to track requirements’ progression and fulfilment throughout the iterative and incremental development process.
In Agile projects involving compliance or regulatory requirements, an explicit traceability matrix can be employed to showcase the development, testing, and acceptance of requirements, ensuring adherence to compliance standards. This enables compliance bodies to track and verify the fulfilment of specific requirements effectively.
Discovering Format of Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM):
As mentioned earlier, the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) format can vary depending on your project’s specific requirements. One example template for the RTM could consist of several key fields. These fields include a unique requirement ID for each requirement, a description of the requirement, the corresponding deliverables, the owner or stakeholder responsible for the requirement, and its current status (e.g., reviewed, approved, rejected).
To facilitate implementation-related traceability, the matrix may also include additional fields. These fields can capture information about the product development stage of each requirement. This allows you to track each requirement’s progress and implementation status throughout the requirements lifecycle. For example, the matrix can include fields to record information about the architecture or design document associated with each requirement, technical specifications, and the test cases linked to each requirement.
Furthermore, the RTM can incorporate fields for verification-related details, allowing you to track each requirement’s validation and verification activities. This can include information such as comments or notes regarding the verification process and any related IDs that establish relationships between different requirements. Utilizing the RTM with these various fields allows you to establish a clear and comprehensive traceability matrix that captures the necessary information for each requirement. This promotes transparency, facilitates effective communication among stakeholders, and enables the establishment of relationships and dependencies between requirements throughout the project.
By maintaining a tabular format, the matrix facilitates the organization and easy navigation, often incorporating filters to manage traceability effectively. You need to discover the best suitable format for your project.
The following videos comprehensively summaries a sample Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) format:
Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) to maximize Business Alignment:
Taking care of Business goals and the need of a requirement is very important. If you see Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) arrangement carefully, it makes you focused on doing activities which are directly related to the reason you are doing requirement-related activities in the project. You have a requirement because there is a need for it. There is a purpose for it, and there is a business alignment. And RTM is the tool to see if stakeholders’ requirements are fitting for the purpose. These stakeholders’ requirements are elaborated in solution requirements, and deliverables are produced. Besides, many work products like test plans and test cases are created. Requirements should be traced from the business goal to the final deliverables, like from the source to its implementation or from the idea to the accepted solution.
So, each Requirement must fit the purpose for business alignment in both traditional predictive methods and Agile approaches, as both types of projects are initiated to address specific business needs.
Traceability and Monitoring using Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM):
A Requirement Traceability Matrix has two components – Traceability and Monitoring. When you look at these two words – Traceability and Monitoring. Traceability is more focused on whether I can trace my requirements end to end. Monitoring is more focused on where I am. So, traceability and monitoring take care of the current status of requirements as well as integrity, relationships, and traceability of requirements. You can put requirements in the middle & there could be a forward as well as backward traceability.
Let’s take one example: There is a Requirement for Login Logout. The technical requirements are discovered for it. T1- The user Id must not be blank. T2: PWD must not be blank. T3: If the user id and PWD are valid, then Login.
Test cases are also created – Say Verify Login – for that, Test steps are created, and Test data is identified. And this is the format of the agreed RTM. You can see RTM can be used to find gaps, like there is no test case written for requirement T1.
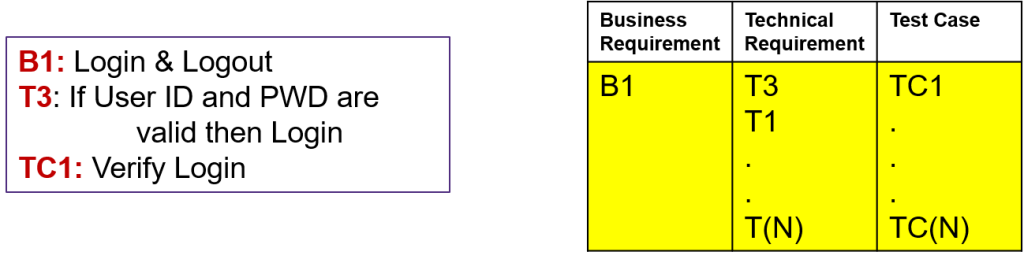
As a general rule, any space in the traceability matrix is a potential area for investigation. At the same time, if any test case is not traced back properly to functional requirements, it is unnecessary. In summary, the process of discovering gaps and extras assists in ensuring that requirements are aligned with their intended purpose. The use of a Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) enables the tracing and monitoring of requirements, ensuring their integrity throughout the requirements life’s current status.
Usage of Requirement Traceability Matrix as a tool for your PMP Exam:
1. Requirement and Scope Validation using Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): Let’s first talk about Requirements validation. Requirement validation ensures that the specified requirements effectively meet the customer’s needs and align with the overall objectives. RTM helps to validate requirements both using backwards and forward traceability. Backward traceability in the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) involves tracing from the middle of the matrix to business needs to understand the necessity of a specific requirement. It examines the requirement connection to the source:
If you go in the forward direction, you trace requirements from the middle of the matrix to its indented deliverables. In forward traceability, you see –
For requirement validation, you may always need more information about a requirement. Sometimes, a stakeholder comes and asks, why do we have this requirement? What value is it adding? So, you can go back, look at the requirement source, and give those answers. Here, RTM is a handy tool to say why we need a particular requirement. Hence serves the purpose of requirement validation.
Scope validation ensures that the project deliverables are completed in alignment with the agreed scope and quality standards. It involves formal acceptance of the deliverables by the customer, confirming their satisfaction with the final outcome. A scope covers deliverables which satisfy specific requirements. During scope validation, the RTM can be used as a reference to review and cross-check each requirement against the completed deliverables. Any gaps or discrepancies between the requirements and the deliverables can be identified through the RTM, allowing for timely corrective actions and adjustments to ensure the scope is properly validated.
2. Managing Change to Requirements using Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM): The Requirement Traceability Matrix is like your trusty sidekick when it comes to managing changes to requirements. Let’s say someone pops up and asks, “Can we just drop this requirement?” Well, you can turn to the RTM and check out its dependencies. By doing so, you can see how removing that requirement could potentially impact other requirements. It’s like playing a game of dominoes – one change can cause a chain reaction of impacts (x, y, z). So, the RTM helps you visualize the ripple effect of changes. Whenever you’re doing impact analysis, the RTM becomes your go-to tool; it helps trace many requirements at once about those relationships and dependencies between requirements. It makes change management a go-to tool for effectively managing changes. It gives information about all related documents and the integrity of these documents and deliverables. All this helps in impact analysis. So, in summary, impact analysis for changes in requirements is all about an integrated approach where the overall impact on cost, schedule, resources, and communications are discovered. Exploring relationships and dependencies using RTM help in doing that.
3. Exploring the status of Requirements using Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM): Tracing requirements helps you in knowing the status of requirements in the requirement life cycle. The requirement life cycle refers to the various stages that a requirement goes through, from its initial suggestion or proposal to its final implementation. The requirement state drives the requirement life cycle. It encompasses the processes involved in capturing, analyzing, documenting, reviewing, approving, and implementing requirements. These are the stages of a requirement that you identify for a requirement. Tracing of requirements gives information about where a particular requirement stands at a moment and shows the status of the requirement. Using RTM, you look at where you are in the requirement life cycle.
Knowing the status of requirements is also crucial for effective communication with stakeholders. When presenting the status of the solution implementation, the project manager or business analysts can provide valuable information by using the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) to indicate the progress made against each requirement. This approach provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of the extent of implementation achieved, allowing for transparent and informative communication about the project’s current state.
When preparing for the PMP exam, keep the following tips in mind regarding the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM):
By focusing on these tips, you will enhance your understanding of the Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) and its significance in project management, improving your chances of success in the PMP exam.
You can watch and listen to the video presentation on more details of the Requirement Traceability Matrix:
In conclusion, this blog aims to provide comprehensive answers to your queries regarding the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) and its significance in Project Management and Business Analysis. By understanding the purpose, benefits, and application of the RTM, you are equipped with a valuable tool to effectively manage requirements, ensure traceability, facilitate change management, validate scope, and communicate with stakeholders. Implementing the RTM can greatly enhance project success and deliver the desired outcomes aligned with customer needs.
If you have aspirations to pursue the PMP certification, enroll with us for comprehensive support in your PMP certification journey. We offer expert guidance in exam preparation, assistance with the application process, and help in scheduling the exam. With our assistance, you can confidently navigate the certification process and increase your chances of success.
iZenBridge offers a wide range of comprehensive FREE resources to support you throughout your PMP certification journey. Explore our PMP Free Practice test, which provides a realistic simulation of the actual exam and helps you assess your preparedness with up-to-date questions. Our 50 Agile PMP Questions tutorial also delves deep into essential PMP Agile concepts, such as working with Requirements, value delivery, Agile Metrics, incremental delivery, and feedback. These tutorials provide detailed explanations and expose you to common Agile-related PMP exam questions. Whether you’re new to Agile or seeking to strengthen your understanding, our scenario-based PMP Agile questions are valuable tools for effective concept comprehension.
| Name | Date | Place | – |
| PMP Certification and Training | 13 – 26 April 2025 | Bangalore | More Details |
| PMP Certification and Training | 10 May – 1 June 2025 | Chennai | More Details |
No Trainings found