
Before we set out to define configuration management, it is crucial to understand why we need it in the first place. How does it come into the play?
Let us consider a situation wherein you are working on one of the work packages. And, looking at the WBS dictionary for acceptance criteria. You have completed the development of the deliverable and sent it to the Quality Control. You are surprised to see that the quality control team rejected the deliverable. They stated that it is not meeting the acceptance criteria.
To clear the confusion, you approach the member of the quality control team. He shows you the WBS Dictionary, where acceptance criteria for the same deliverable are different. You concluded a thorough analysis of the situation. And, got to know that you were using the old version of the WBS Dictionary. To avoid such issues in the future, you need a concrete system called Configuration Management.
Now the question is, what is Configuration Management in a project? Why it is important?
PMBOK® Guide Sixth Edition Defines Configuration Management as
A subsystem of the overall project management system. It is a collection of formal documented procedures used to apply technical and administrative direction and surveillance to recognize and document the functional and physical characteristics of a product, result, service, or component; control any changes to such characteristics; record and report each change and it is implementation status; and support the audit of the products, results, or components to verify conformance to requirements. It includes the documentation, tracking systems, & defined approval levels necessary for authorizing & controlling changes.
Let’s discuss one point at a time; this would make it easier to understand the definition:
Now the question is how to implicate these points in a Project?
We need to first start from Configuration management planning, and the result of this planning could be Configuration management Plan.
PMBOK® Guide Sixth Edition Defines Configuration management plan as,
“The configuration management plan defines those items that are configurable, those items that are require formal change control, & the process for controlling changes to such items.”
Configuration Planning tells us the following:
Configuration Management Plan also recommends:
In the configuration management plan, we define a clear versioning system. It helps in the identification of baseline CIs. Like, when we have many version of Project Scope Statement, it helps to get a baseline version of Project Scope Statement.
Also, a Configuration management plan may go beyond project boundaries. Since the product we are developing may already be in existence before the project commenced. And it may also remain in existence after the project is over. A product life cycle may include many project life cycles.. In some cases, configuration management system is highly influenced by the product level configurations. And, we end up having two views of configuration management –
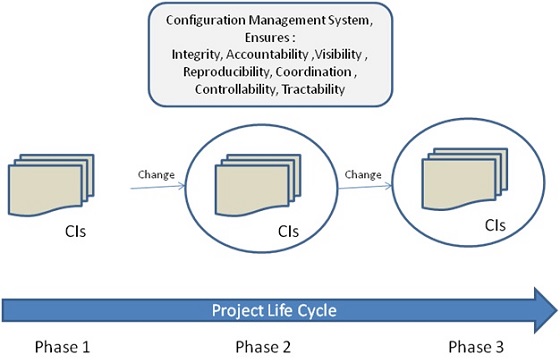
The configuration management system is a subsystem of overall project management. The goal of this subsystem is to manage fundamental project constraints of scope, time, cost and quality. It is an environment needed to apply change management processes to admin all changes related to the organization (project).
We do Configuration management activities in the Perform Integrated Change Control Process. This process includes the following configuration management activities:
During configuration management planning, we identify CIs. And, while performing an integrated change control process-
We need to make sure to follow the configuration management plan for those CIs. And, as the configuration management plan records the physical and functional characteristics –
This process controls changes to these characteristics based on CMS. It helps in maintaining the integrity of those CIs.
The goal of configuration status accounting is to maintain an audit trail and artifacts of all changes, including all versions of CIs. It also shows the status of each version. The status may say the following:
Let’s take an example:
If I am approving the change in the scope statement –
I need a record that the new version of this document would be coming for this approved change. And, after change implementation, the Configuration Management system will ensure that everybody gets the latest version.
We can consider Configuration status accounting as like recording the changes as they are taking place as per the configuration management plan. Like, changing the version, maintaining the version history, etc.
Following is the goal of configuration verification and audit:
It ensures that we build project CIs according to their defined documentation. These are formal audits usually conducted at least once for each release.
Now, the question is, why do we need configuration verification and audit?
We need it because:
At a defined frequency, the project team should have a process to verify and audit that configuration management plan which should be followed. Some of the verification points could be:
It is not a replacement of existing reviews, inspections. It is like quality assurance team visits and formally audit to see if the Configuration management plan is followed.
PMBOK® Guide Sixth Edition defines Configuration Verification and Audit as,
To summarize, the entire Configuration Management process can be viewed as:
Also, it is crucial to understand that we don’t follow formal change for all the artifacts. It is not needed, we need to invest our energy wisely. Let’s take an example – In a project, we feel that we need formal change control for the WBS dictionary. The reason could be like many other CIs are depend on it, like
On the other hand, when we are adding or removing issues from issue log – we don’t have any direct impact. So, we decided not to do formal change control for it.
Here, next question arises – what is the difference between configuration management plan and change management plan?

Configuration management is an umbrella which includes change management. When a change is requested, we need to make sure physical and functional characteristics of CI based on Configuration management plan. And, the change request is approved or rejected based on the change management plan.
According to the Practice Standard for Project Configuration Management (On page number 17) configuration change management can be viewed as follows:
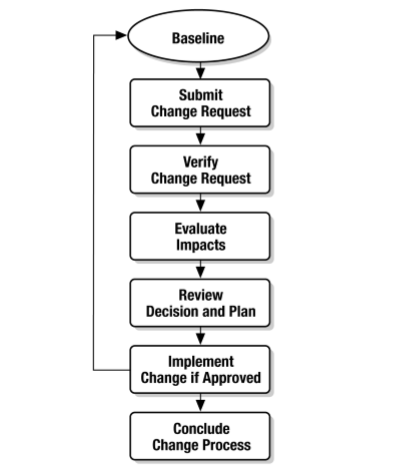
Configuration change management is usually described in the project change control plan or in a separate configuration management plan if project size and complexity justify it.
You can watch and listen to the live video presentation on configuration management here. It will help you with practical examples about how you can see the configuration management system in your project:
By now you must have completely understood the basic concepts underlying the configuration management and how does it impact the software project. Good Luck for your PMP® Certification Exam.
You can join the discussion on the same in our Forum You can also log into our YouTube channel watch the video on the configuration management.
Enroll to our FREE PMP® Certification Introductory Program to learn more about PMP® certification
| Name | Date | Place | – |
| PMP Certification and Training | 13 – 26 April 2025 | Bangalore | More Details |
| PMP Certification and Training | 10 May – 1 June 2025 | Chennai | More Details |