

EAC (Estimate at Completion) and ETC (Estimate to Complete) are indeed essential dimensions of Earned Value Management (EVM). They play a crucial role in project management and are important concepts to understand for PMP exam preparation. They help assess the project’s performance and forecast future costs and completion dates.
When discussing EVM estimates, we make projections or forecasts indicating a deviation from the original plan (BAC – Budget at Completion). It is because plans often need to be revised as projects progress as they may encounter unforeseen circumstances. EAC represents a revised estimate of the total cost budget based on the current situation.
Understanding EAC in the PMP Exam: Estimate at Completion in Earned Value Management (EVM)
In the context of the PMP exam, Estimate at Completion (EAC) refers to the anticipated total cost required to complete all the work. It is calculated by summing up the actual cost incurred to date with the estimate to complete the remaining work.
So, EAC is a forecast of the total project cost at completion. It considers the actual performance data and any variances that have occurred. EAC is useful for assessing the overall project performance and determining if the project will be over or under budget at completion.
ETC in the PMP Exam: Understanding Estimate to Complete (ETC) in Earned Value Management (EVM)
Estimate to Complete is the expected cost to finish all the remaining project work.
So, ETC represents the forecasted cost required to complete the remaining project work. It helps assess how much additional funding will be needed to complete the project. ETC considers the actual performance data and estimates the future cost based on the current trends.
The most common formula for calculating ETC is:
ETC = EAC – AC
This formula subtracts the actual cost (AC) incurred so far from the estimate at completion (EAC) to determine the additional cost required.
Here are some important points about Estimate at Completion (EAC) and Estimate to Complete (ETC) that are often overlooked:
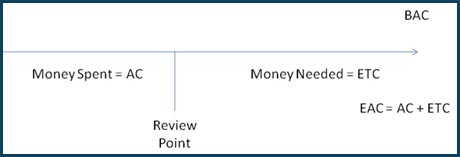
When calculating forecasts such as EAC (Estimate at Completion) and ETC (Estimate to Complete), it is crucial to keep in mind that the actual costs (AC) already incurred are irreversible and cannot be recovered. The focus should be on estimating the remaining work based on the current project situation. The ETC represents the expected cost needed to complete the remaining work. By summing up the actual costs (AC) with the Estimate to Complete (ETC), we arrive at the Estimate at Completion (EAC) formula: EAC = AC + ETC.
The biggest project management questions a project manager must always answer is how much more money this project will cost. Which is ETC, but how to find that out? How does the project manager figure out the money needed for the remaining work? There is no magical formula based on the project stage and variance. Earned value management suggests ways of calculating the ETC. Let’s consider the cases.
I trust that this blog has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of EAC (Estimate at Completion) and ETC (Estimate to Complete), as well as the significance of AC (Actual Cost) in their calculations. If you have any further questions or would like to discuss this topic further, please feel free to leave your comments in the box below. For a visual representation of these concepts, I recommend watching the following video:
If you have aspirations to pursue the PMP certification, enroll with us for comprehensive support in your PMP certification journey. We offer expert guidance in exam preparation, assistance with the application process, and help in scheduling the exam. With our assistance, you can confidently navigate the certification process and increase your chances of success.
iZenBridge offers a wide range of comprehensive FREE resources to support you throughout your PMP certification journey. Explore our PMP Free Practice test, which provides a realistic simulation of the actual exam and helps you assess your preparedness with up-to-date questions. Our 50 Agile PMP Questions tutorial also delves deep into essential PMP Agile concepts, such as working with Requirements, value delivery, Agile Metrics, incremental delivery, and feedback. These tutorials provide detailed explanations and expose you to common Agile-related PMP exam questions. Whether you’re new to Agile or seeking to strengthen your understanding, our scenario-based PMP Agile questions are valuable tools for effective concept comprehension.
