

Lead and Lag in project activities are easy concepts. Even though, during my coaching sessions, I see a lot of confusion around them. Especially when we use these concepts in –
Network diagrams and with a different type of relationships.
Let’s decode these confusions here starting from Lag time in project management.
Based on PMBOK® Guide Sixth Edition
A lag time is the amount of time whereby a successor activity is required to be delayed with respect to a predecessor activity.
Following are Important points about this definition which many of us tend to miss. These points are the main source of confusions.
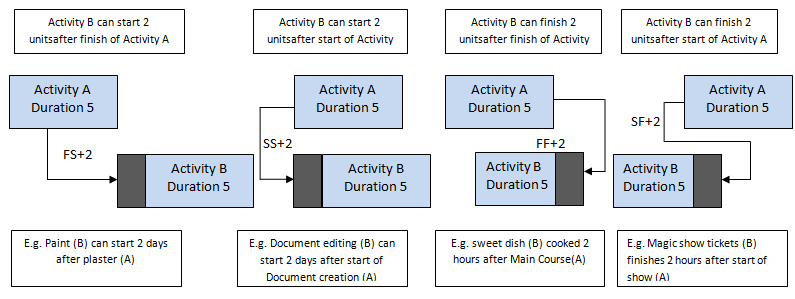 All these aspects of Lag, we can put for Lead too. Let’s see how
All these aspects of Lag, we can put for Lead too. Let’s see how
What is lead time in project management?
Based on PMBOK® Guide Sixth Edition
Following are the key points from this definition:
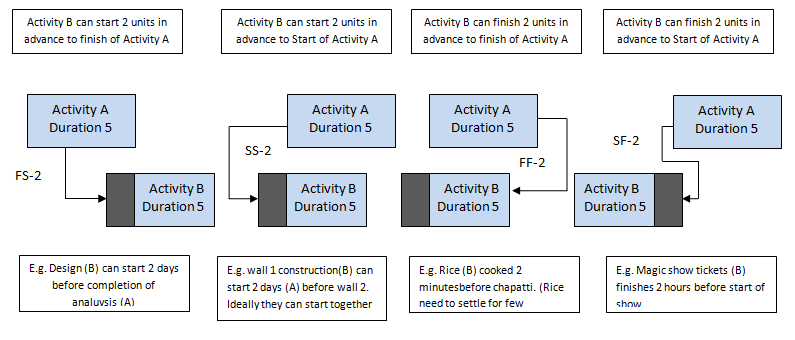 After handling so many questions on Lead and Lag, I realized the main point to fail is:
After handling so many questions on Lead and Lag, I realized the main point to fail is:
Visualize the situation to apply one type of dependency along with relationships.

A: We need to remember –
For relationship first letter defines predecessor behavior and second successor. E.g., for Finish to Start, Finish of predecessor and start of successor dependency. We need to start reading it that way.
A: “+” is used for lag and “–“ is used for lead. E.g. if the relationship is SS+2, naturally we should read it as Start of Activity B with Lag of 2 with respect to start of Activity A.
A: It varies. It’s applied due to the predefined constraint (in case of Lag majorly). And sometimes we use it to achieve project deadlines (In case of Lead)
A: Lead is a type of dependency. And, we use Lead while fast-tracking schedule compression technique. Many times, we need to reschedule activities which are happening in serial. Using fast-tracking, we make them happen in parallel. So, we can meet the deadlines. Lead in network diagram helps in achieving that.
For more details on Lead and Lag with practical examples, simple watch following video:
This is precisely the compilation of Lead and Lag on the whole. Good Luck with your PMP® Certification Exam. Happy reading and do post follow up questions here on our DISCUSSION FORUM
Enroll to our FREE PMP® Certification Math Program to learn more about this topic
Enroll to our FREE PMP® Certification Introductory Program to learn more about PMP® certification
| Name | Date | Place | – |
| PMP Certification and Training | 15 – 30 November 2025 | Bangalore | More Details |
| PMP Certification and Training | 9 Dec’25 – 7 Jan’26 | Chennai | More Details |